2026
A paper about Zeroth-order optimization on the edge devices
Yihang Zuo, etc.
Submitted to ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC)
A paper about Zeroth-order optimization on the edge devices
Yihang Zuo, etc.
Submitted to ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC)
2025
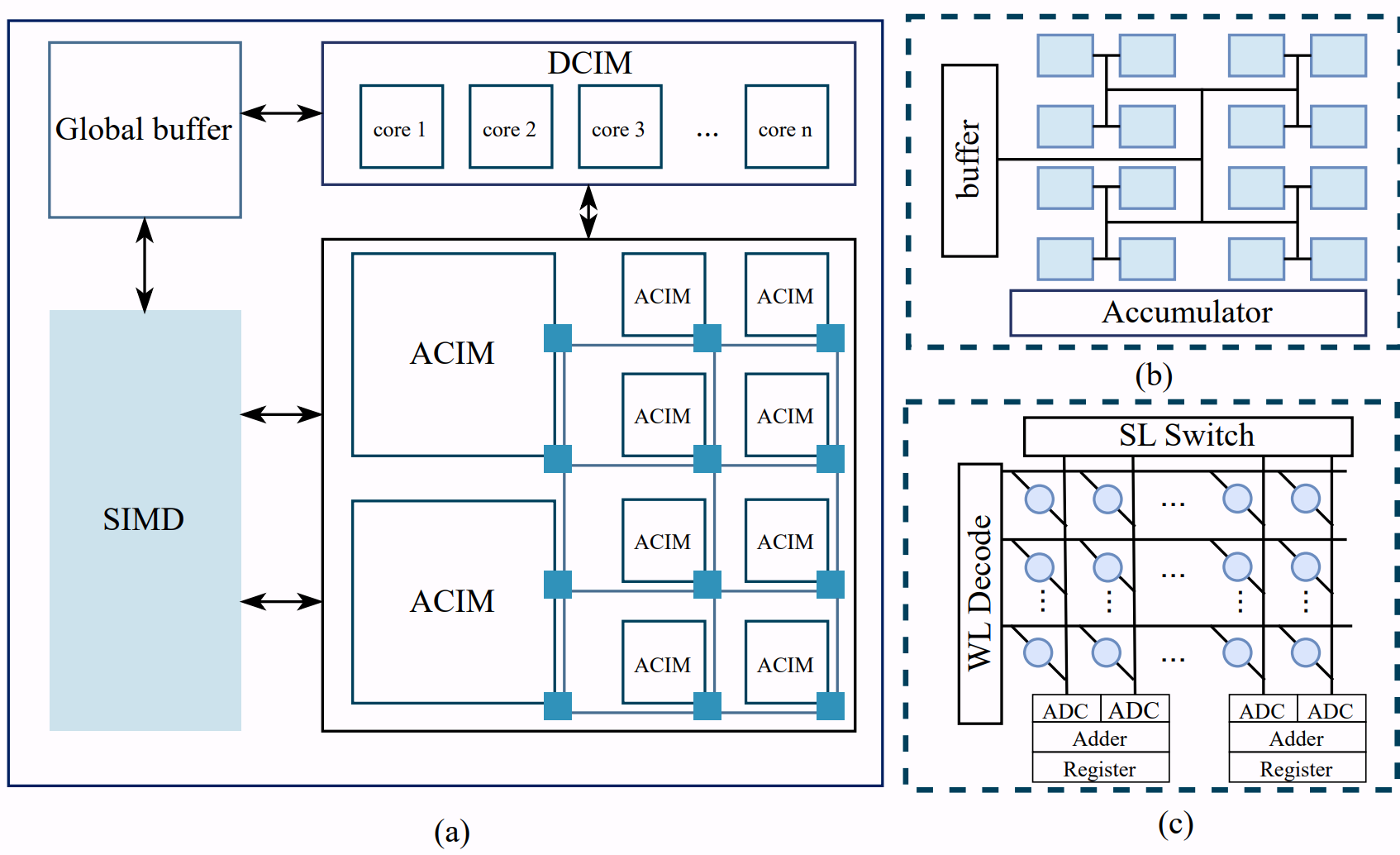
Harmony: A Hardware-Mapping Co-Exploration Framework for Hybrid CIM-based Vision Transformer Accelerator
Yihang Zuo, Zexin Fu, Cong Wang, Yuchao Wu, Jiayi Huang, Yuzhe Ma
International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED) 2026
Computing-in-memory (CIM) architectures have successfully enhanced convolutional neural network (CNN) performance, but the automation of high-performance CIM-based transformer accelerators is still challenging. Specifically, the design space of hardware design and mapping is extremely large due to the complex model structure and data flow. To address this problem, we propose Harmony, a hardware and mapping co-exploration framework to optimize the hybrid CIM-based vision transformer accelerator. We define a universal design space representation for implementing vision transformers in CIM-based accelerators that support hybrid and heterogeneous features. The corresponding design space comprises the hardware configuration of CIM macros and their spatial mapping scheme. Furthermore, we propose the knowledge-guided grid search (KGGS) algorithm and improved genetic algorithm (IGA) to boost exploration efficiency. The orthogonal experiment and dominance analysis of KGGS could obtain the exploration probabilities of different parameters and ensure its stability, while the unique order crossover and swapping mutation of IGA could retain relative order to avoid legalization processes during the iteration.
Harmony: A Hardware-Mapping Co-Exploration Framework for Hybrid CIM-based Vision Transformer Accelerator
Yihang Zuo, Zexin Fu, Cong Wang, Yuchao Wu, Jiayi Huang, Yuzhe Ma
International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED) 2026
Computing-in-memory (CIM) architectures have successfully enhanced convolutional neural network (CNN) performance, but the automation of high-performance CIM-based transformer accelerators is still challenging. Specifically, the design space of hardware design and mapping is extremely large due to the complex model structure and data flow. To address this problem, we propose Harmony, a hardware and mapping co-exploration framework to optimize the hybrid CIM-based vision transformer accelerator. We define a universal design space representation for implementing vision transformers in CIM-based accelerators that support hybrid and heterogeneous features. The corresponding design space comprises the hardware configuration of CIM macros and their spatial mapping scheme. Furthermore, we propose the knowledge-guided grid search (KGGS) algorithm and improved genetic algorithm (IGA) to boost exploration efficiency. The orthogonal experiment and dominance analysis of KGGS could obtain the exploration probabilities of different parameters and ensure its stability, while the unique order crossover and swapping mutation of IGA could retain relative order to avoid legalization processes during the iteration.
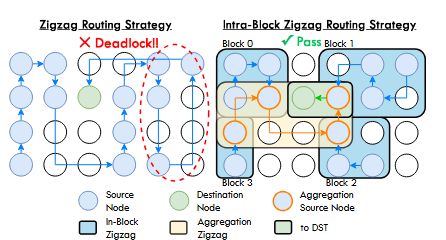
Optimizing Heterogeneous Compute-in-Memory with Hybrid Dataflow and In-Network Reduction for Vision Transformer
Zexin Fu, Yihang Zuo, Yuzhe Ma, Jiayi Huang
International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED) 2025
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown remarkable success in computer vision tasks, but their computational demands pose significant challenges for efficient deployment. This paper presents an optimization framework for heterogeneous Compute-in-Memory (CIM) architectures that leverages hybrid dataflow and in-network reduction techniques to accelerate ViT inference. Our approach addresses the unique computational patterns of ViTs by combining different dataflow strategies and implementing efficient reduction operations within the CIM network.
Optimizing Heterogeneous Compute-in-Memory with Hybrid Dataflow and In-Network Reduction for Vision Transformer
Zexin Fu, Yihang Zuo, Yuzhe Ma, Jiayi Huang
International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED) 2025
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown remarkable success in computer vision tasks, but their computational demands pose significant challenges for efficient deployment. This paper presents an optimization framework for heterogeneous Compute-in-Memory (CIM) architectures that leverages hybrid dataflow and in-network reduction techniques to accelerate ViT inference. Our approach addresses the unique computational patterns of ViTs by combining different dataflow strategies and implementing efficient reduction operations within the CIM network.
2024
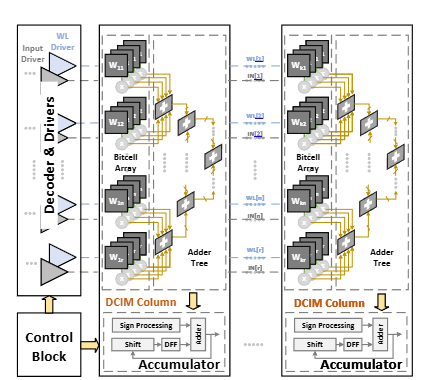
OpenC2: An Open-Source End-to-End Hardware Compiler Development Framework for Digital Compute-in-Memory Macro
Tianchu Dong, Shaoxuan Li, Yihang Zuo, Hongwu Jiang, Yuzhe Ma, Shanshi Huang
Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference (DATE) 2024
Compute-in-Memory (CIM) has emerged as a promising paradigm to address the memory wall problem in modern computing systems. However, the lack of comprehensive toolchains for CIM macro development hinders its widespread adoption. This paper presents OpenC2, an open-source end-to-end hardware compiler development framework specifically designed for digital CIM macros. OpenC2 provides a complete toolchain from high-level algorithm descriptions to optimized CIM macro implementations, enabling rapid prototyping and design space exploration.
OpenC2: An Open-Source End-to-End Hardware Compiler Development Framework for Digital Compute-in-Memory Macro
Tianchu Dong, Shaoxuan Li, Yihang Zuo, Hongwu Jiang, Yuzhe Ma, Shanshi Huang
Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference (DATE) 2024
Compute-in-Memory (CIM) has emerged as a promising paradigm to address the memory wall problem in modern computing systems. However, the lack of comprehensive toolchains for CIM macro development hinders its widespread adoption. This paper presents OpenC2, an open-source end-to-end hardware compiler development framework specifically designed for digital CIM macros. OpenC2 provides a complete toolchain from high-level algorithm descriptions to optimized CIM macro implementations, enabling rapid prototyping and design space exploration.
2023
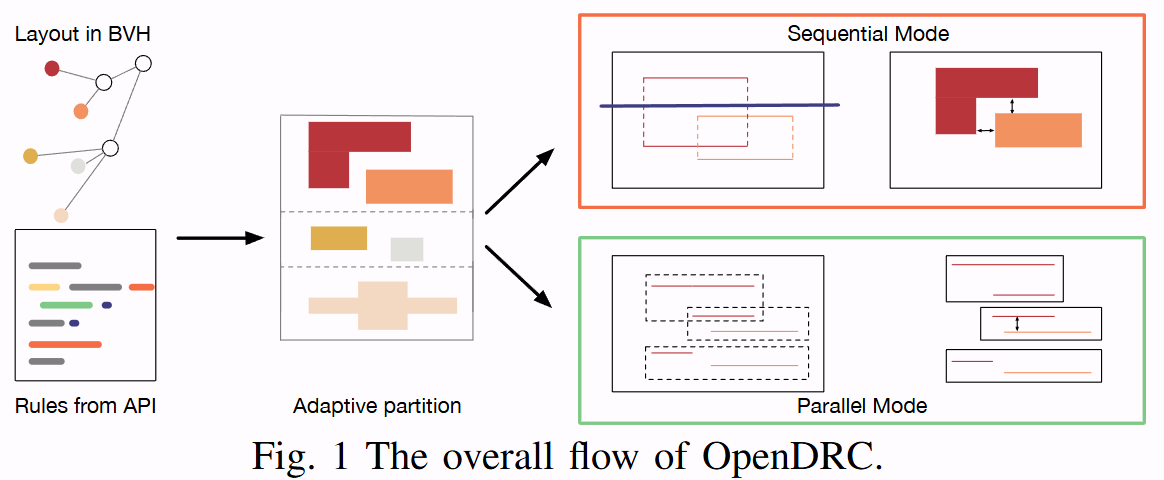
OpenDRC: An Efficient Open-Source Design Rule Checking Engine with Hierarchical GPU Acceleration
Zhuolun He, Yihang Zuo, Jiaxi Jiang, Haisheng Zheng, Yuzhe Ma, Bei Yu
ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC) 2023
Design Rule Checking (DRC) is a critical step in the VLSI design flow that ensures manufacturability of integrated circuits. Traditional DRC tools face scalability challenges with increasing design complexity. This paper presents OpenDRC, an efficient open-source DRC engine that leverages hierarchical GPU acceleration to achieve significant performance improvements. Our approach utilizes the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs and hierarchical design representation to accelerate DRC operations while maintaining accuracy.
OpenDRC: An Efficient Open-Source Design Rule Checking Engine with Hierarchical GPU Acceleration
Zhuolun He, Yihang Zuo, Jiaxi Jiang, Haisheng Zheng, Yuzhe Ma, Bei Yu
ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC) 2023
Design Rule Checking (DRC) is a critical step in the VLSI design flow that ensures manufacturability of integrated circuits. Traditional DRC tools face scalability challenges with increasing design complexity. This paper presents OpenDRC, an efficient open-source DRC engine that leverages hierarchical GPU acceleration to achieve significant performance improvements. Our approach utilizes the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs and hierarchical design representation to accelerate DRC operations while maintaining accuracy.
2022
Symmetrical indoor visible light layout optimized by a modified grey wolf algorithm
Yihang Zuo, Bojun Liu, Kunming Shao
Applied Optics (AO) 2022
Visible light communication (VLC) systems require optimal LED placement to ensure uniform illumination and reliable communication. This paper presents a modified grey wolf optimization algorithm for designing symmetrical indoor visible light layouts. The proposed approach optimizes LED positioning to achieve balanced illumination distribution while maintaining communication quality, addressing the challenges of indoor VLC system design.
Symmetrical indoor visible light layout optimized by a modified grey wolf algorithm
Yihang Zuo, Bojun Liu, Kunming Shao
Applied Optics (AO) 2022
Visible light communication (VLC) systems require optimal LED placement to ensure uniform illumination and reliable communication. This paper presents a modified grey wolf optimization algorithm for designing symmetrical indoor visible light layouts. The proposed approach optimizes LED positioning to achieve balanced illumination distribution while maintaining communication quality, addressing the challenges of indoor VLC system design.
2021

Analysis on Public Opinion Sentiment Evolution of COVID-19 Based on Weibo Data
JiangPing Wan, Xu Liu, Yihang Zuo, Jianfeng Luo
WHICEB 2021 PROCEEDINGS 2021
Understanding public sentiment evolution during major events like the COVID-19 pandemic is crucial for effective crisis management. This paper analyzes public opinion sentiment evolution of COVID-19 based on Weibo (Chinese social media platform) data. We employ natural language processing techniques to track sentiment changes over time and identify key factors influencing public opinion during different phases of the pandemic.
Analysis on Public Opinion Sentiment Evolution of COVID-19 Based on Weibo Data
JiangPing Wan, Xu Liu, Yihang Zuo, Jianfeng Luo
WHICEB 2021 PROCEEDINGS 2021
Understanding public sentiment evolution during major events like the COVID-19 pandemic is crucial for effective crisis management. This paper analyzes public opinion sentiment evolution of COVID-19 based on Weibo (Chinese social media platform) data. We employ natural language processing techniques to track sentiment changes over time and identify key factors influencing public opinion during different phases of the pandemic.